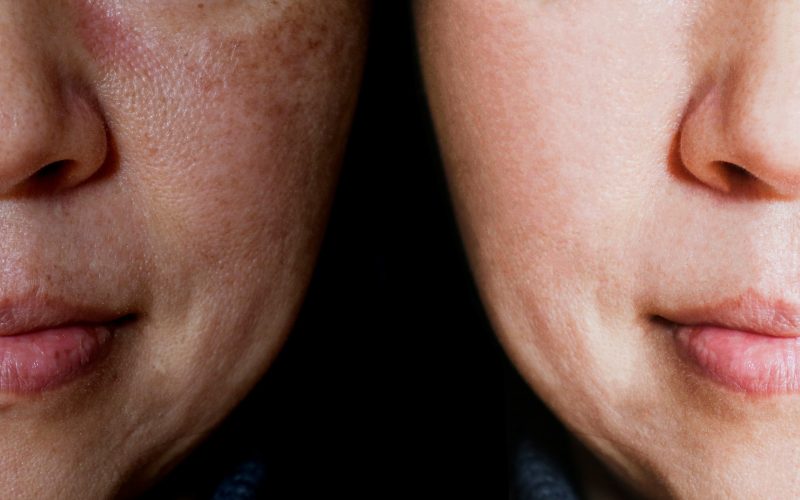
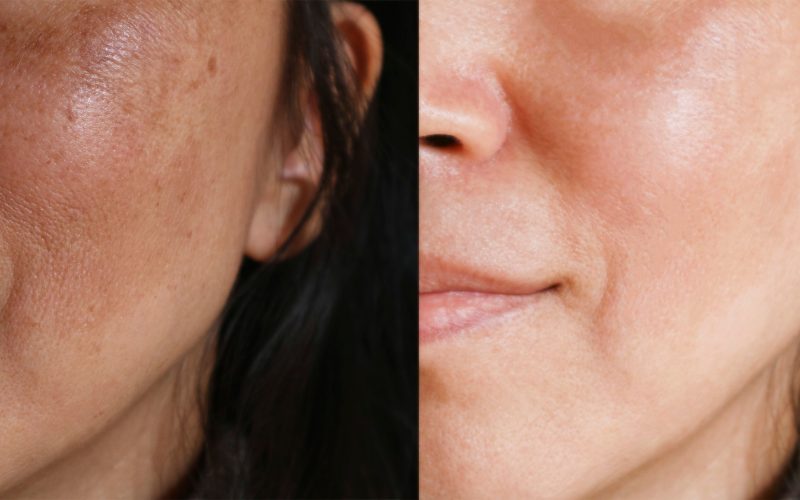
Melasma: Top 8 Treatment Options
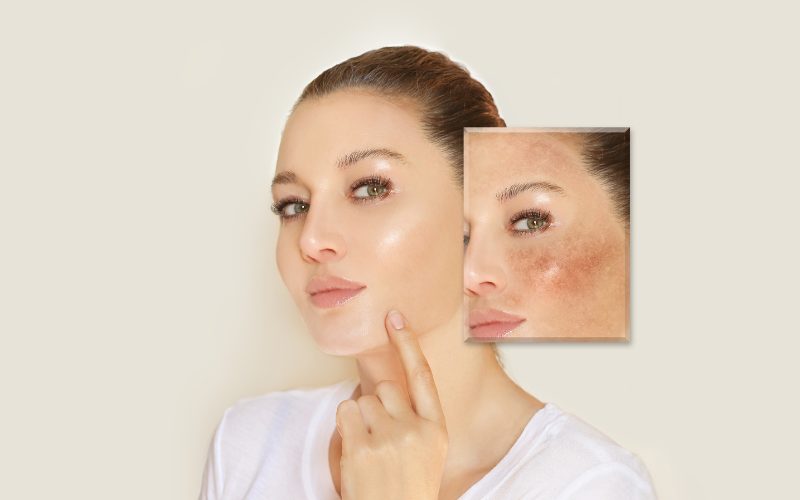
Melasma, also known as the “mask of pregnancy,” is a skin condition that causes brown or gray patches on your face. It can be an embarrassing and frustrating condition because it can affect anyone at any age, and there are no known triggers. Melasma usually disappears within six months after you give birth or stop taking hormones. However, if melasma doesn’t go away after several months—or if it comes back when you get pregnant again—you may need more aggressive treatment options than sunscreen. Here are eight treatments for melasma.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition that causes dark patches on your face and neck. It’s also known as chloasma, or the mask of pregnancy. Melasma is caused by the overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color. The dark patches are called hyperpigmentation and can be permanent. You can get melasma at any age, but it’s most common in pregnant women or taking birth control pills.
Melasma occurs when your body makes too much melanin, a pigment in your skin cells that gives them their color. When there’s too much melanin production, it can lead to brown patches on your face and neck.
You may have heard of melasma being referred to as “the mask of pregnancy” because many pregnant women develop these patches during their pregnancies (but not all do). It’s also sometimes called chloasma (pronounced klo-az’ma), which comes from the Greek word for yellow.
1. Sunscreen
When it comes to melasma, the most important thing you can do is use sunscreen daily. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 every day, even when inside or in the shade. UVA rays (also partially responsible for melasma) can penetrate through clouds, so ensuring your skin is protected throughout the day is essential.
Sunscreen should be applied generously and often reapplied—every two hours if you’re sweating or swimming, and after 80 minutes of direct sunlight exposure if not—to ensure that it effectively protects against both UVA and UVB radiation from reaching your skin.
In addition to its role in preventing further damage from occurring on top of existing melasma spots, daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen may also help fade existing melasma spots over time by blocking out some of the sun’s harmful rays before they have a chance to cause damage on top of existing pigmentation issues.
There are many types of sunscreen to choose from, including physical sunblocks such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide and chemical sunscreens like avobenzone. A physical sunscreen will sit on top of your skin and deflect some of the sun’s rays before they can penetrate deep into your tissue; this is why it’s essential to apply these products generously so that they can fully cover all exposed areas.
Chemical sunscreens absorb UV radiation before it reaches your skin and can cause damage. The downside of chemical sunscreens is that they tend to be more irritating than physical sunblocks; it’s crucial to find a sunscreen formula that doesn’t bother your skin too much when you apply it.
2. Retinoids
Retinoids can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other treatments, depending on the severity of your melasma. Retinoids are derived from vitamin A and help regulate the production and release of pigment within your body. They are often prescribed for acne, but they also work for hyperpigmentation.
Retinoids come in different forms: retinoic acid (tretinoin), tazarotene, adapalene/differin, and epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) inhibitors like topical tacrolimus ointment or pimecrolimus cream. The most common side effects include stinging, burning, and redness that typically subsides over time once your skin gets used to the medication.
You can avoid these side effects by applying retinoid creams at night when you’re not exposed to sunlight or UV rays, using sunscreen during the day, and avoiding using products containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid. You should also reduce your exposure to the sun while using this drug and avoid large amounts of alcohol while taking this medication because it increases flushing.
Avoid simultaneous use with other drugs with photosensitizing properties, such as tetracycline antibiotics, because both increase photosensitivity when combined. Avoid using topical retinoids if you have sensitive skin or a history of eczema.
You can also prevent retinoids’ side effects by slowly decreasing your dosage over time and starting with a small amount. When used in combination with other medications, avoid using them at the same time as each other.
3. Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is a chemical exfoliant that can be used to treat melasma. This chemical peel helps decrease the appearance of dark patches by removing the top layer of skin, revealing lighter-colored skin underneath it. It’s important to note that glycolic acid peels are not recommended for pregnant women or those with darker skin tones due to the risk of hyperpigmentation (darkening).
Glycolic acid peels come in strengths ranging from 20% to 70%, but it’s generally recommended that you start with a lower percentage and increase it if needed. A typical treatment protocol might look like this:
- First treatment: 25% solution applied every week for three weeks (or until results are reached)
- Subsequent treatments: 15% solution applied every week for three weeks (or until results are reached)
The time it takes to see results will vary depending on your skin type, but many people see improvements within a couple of weeks. The best way to determine if a chemical peel is right for you is to consult a dermatologist or plastic surgeon.
4. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive treatment that exfoliates the skin. It can help with melasma, but it’s important to note that it’s also used to treat acne, scars, and wrinkles. This treatment can be done at home or by professionals. However, if you’re going to do it yourself, you must purchase professional equipment designed specifically for this purpose.
The procedure is pretty simple, but taking some precautions is essential. The first thing you should do is check the equipment for any cracks or damage. If there’s any doubt about its safety, don’t use it! You’ll also want to wear protective clothing; preferably a lab coat or smock, to keep your clothes clean and free of particles.
The next thing you’ll want to do is wash your face with soap and water, then dry it thoroughly. Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly around your eyes, lips, nose and ears; this will help protect these sensitive areas from any damage caused by the procedure. Now you’re ready to start!
5. Fractional Laser
Fractional lasers are a type of laser that uses multiple micro-thermal columns to break up the pigment in the skin. They can be used to treat melasma but also other conditions such as acne scars and stretch marks. Fractional lasers target areas of excess melanin in your skin and destroy them without damaging surrounding tissue.
This treatment is effective for all skin types. It is safe for people with darker complexions because it targets only the pigmented cells without affecting your entire epidermis (the top layer of your skin). The treatment is also less painful than other lasers and has no downtime. The procedure can be performed in about an hour, and most patients can return to work or school the next day.
In addition to reducing the appearance of wrinkles, you can also have your face and neck exfoliated with this treatment. This will leave your skin looking smoother and more radiant than before. Fractional lasers are ideal for those who want to improve their appearance without having any downtime associated with other lasers.
The procedure can be performed in about an hour, and most patients can return to work or school the next day. In addition to reducing the appearance of wrinkles, you can also have your face and neck exfoliated with this treatment. This will leave your skin looking smoother and more radiant than before. Fractional lasers are ideal for those who want to improve their appearance without having any downtime associated with other lasers.
6. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are a good option for treating melasma. However, chemical peels can be very aggressive, and you should only get them done by a dermatologist. Chemical peels can be done in a professional setting or at home. Whichever option you choose, you must ensure that your doctor or aesthetician has experience with chemical peels and that they have the right equipment and products to give you the best results.
Chemical peels are not recommended for people with darker skin tones, as they can cause discoloration. If you decide to get a chemical peel, you should only have it done by a dermatologist or other medical professional specializing in treating melasma.
The best way to treat melasma is with a combination of treatments. Spot treatments are excellent for treating individual dark spots and should be used in addition to other treatments, like creams and chemical peels.
7. Dermaplaning
Dermaplaning is a treatment that uses a scalpel to scrape away the outermost skin layer. It’s similar to microdermabrasion, but instead of using suction or an abrasive substance to remove dead skin cells, dermaplaning uses a blade to shave off the outermost layer of skin gently. The process can be done at home with an at-home device or in your dermatologist’s office under their supervision.
Dermaplaning can be used on all skin types and all areas of the face, including around the mouth, eyebrows, forehead, and nose. However, it will not work for deeper wrinkles, such as those around the eyes or lips, because these require deeper penetration for results.
It’s best used on dry skin since any moisturizer will interfere with its effectiveness. However, suppose you’re using prescription retinoids such as Tazorac.
You should wait until they are entirely absorbed before you do so because they will make your skin more sensitive than usual during this period. Also, remember that during your first few sessions, you may experience some redness, but this should subside within 10 minutes after completing each session and should not last longer than 24 hours.
8. Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a prescription skin-lightening agent. It’s typically used in combination with other treatments to treat hyperpigmentation. Hydroquinone works by blocking the production of melanin and reducing excessive pigmentation.
It can cause side effects, including allergy and irritation, which may make it problematic for some people to use it on their skin; however, most people tolerate hydroquinone well when applied as directed by their doctor or dermatologist. Hydroquinone is available as a cream, gel, or lotion. It’s often used in combination with other skin-lightening agents.
Hydroquinone is a prescription skin-lightening agent. It’s typically used in combination with other treatments to treat hyperpigmentation. Hydroquinone works by blocking the production of melanin and reducing excessive pigmentation.
It can cause side effects, including allergy and irritation, which may make it problematic for some people to use it on their skin; however, most people tolerate hydroquinone well when applied as directed by their doctor or dermatologist.
How Long Does It Take To Treat Melasma?
Melasma can be treated, but it will take time. It can take anywhere from a few months to a year or more, depending on the severity of your melasma and how quickly your body responds to treatment.
There are many different treatment options for melasma, but most require multiple treatments to see results. The duration of each treatment depends on the type of treatment you receive and how much sun exposure you have had before starting treatment.
The best way to know how long melasma treatment will take is to speak with your doctor about the results you can expect based on your skin tone and the severity of your condition.
Conclusion
Melasma is a skin condition that affects millions of people. It can be treated with various medications and therapies, but they are not all equally effective. So how do you know which treatment option is right for your particular needs? The best way to start is by consulting with a dermatologist who specializes in treating this condition so that they can evaluate whether their methods would be effective on your unique case.