How To Treat Melasma: 15 Helpful Tips
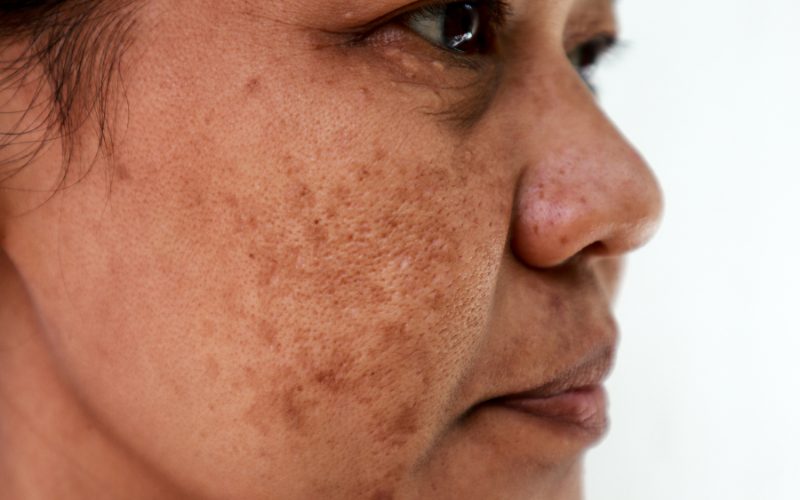
Melasma, also called the mask of pregnancy, is a darkening of the skin on sun-exposed areas. Melasma is most common in women and can occur during pregnancy. It can also affect people with darker skin tones more than people with lighter complexions. The good news is that many different treatment options are available to help you get rid of melasma and reclaim your beautiful skin tone.
How To Treat Melasma In 10 Ways
Here are ten ways to treat melasma.
1. OTC Creams And Lotions
As with most skin conditions, OTC creams and lotions can be a practical first step in treating melasma. They are easy to find and inexpensive, making them an excellent place to start if you’re out of options. However, these products may not work for severe cases of melasma. Some people find that they irritate the skin or don’t provide enough coverage; others prefer prescription treatments over OTCs.
Regardless of your preferences, you must do some research before using any topical product on your face (or any part of your body). If a product claims to treat melasma without any evidence backing up its effectiveness, then steer clear!
2. Prescription Creams
Prescription creams are often the most effective treatment for melasma. They can be more effective than over-the-counter products and may have fewer side effects. But they’re also more expensive and have to be prescribed by a doctor who can monitor you closely.
Prescription creams include:
- Hydroquinone is available in 2%, 4%, or 5% strengths (skin lightening). This is usually applied twice daily to affected areas of the skin until your melasma clears up. The most common side effect of hydroquinone is skin irritation or redness, but some people develop an allergic reaction called exogenous ochronosis after using it long-term. If this happens to you, stop using hydroquinone immediately! You should also see a doctor immediately if you develop dark spots after stopping use (this could mean that your skin has become dependent on lightening).
- Retinoids like retinol, tretinoin (Retin-A), adapalene (Differin), and tazarotene (Tazorac) can help with pigment production under the surface of the skin—but there are risks involved: these medications can cause contact dermatitis and increase your susceptibility to sunburns while they work their magic! Retinoids should be used with caution by people who have sunburns quickly, have sensitive skin, or have had previous allergic reactions to vitamin A products.
3. Birth Control
Birth control pills can help reduce the severity of melasma. However, this treatment may not be effective in all women and should be used cautiously. Birth control pills contain estrogen and progesterone, hormones essential to your body’s normal functioning. The purpose of using birth control pills is to prevent pregnancy by manipulating these hormones to prevent ovulation (the release of an egg).
Because birth control pills contain estrogen, they may cause side effects such as headaches or breast tenderness that could make you feel less comfortable taking them long-term.
4. Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal treatments are one of the most common options for treating melasma. Your doctor will prescribe birth control pills or estrogen and progesterone creams in these cases. Hormone therapy is designed to reduce your skin’s production of melanin, which can help reduce or eliminate melasma.
The downside is that hormonal treatments can cause side effects such as headaches and breast tenderness. Your doctor may recommend a different treatment if you have these symptoms or if other treatments haven’t worked well for you.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs are an effective treatment for melasma. They have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and can reduce melanin production, which is why they’re used in many skin-care products.
- Commonly used anti-inflammatory drugs include diclofenac, ibuprofen, or aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). These medications should be taken only if you have a doctor’s prescription because they can cause stomach bleeding and other side effects. Taking these drugs may also trigger a headache or low blood pressure, so if either occurs, you should immediately stop using them and see your doctor as soon as possible.
- You should take 500 milligrams of ibuprofen (Advil) every six hours until your symptoms improve, then switch to 200 milligrams every six hours until you no longer need it. You’ll want to avoid taking more than 1,000 milligrams daily; exceeding this limit can damage your liver over time.
- Diclofenac comes in pill form and as a gel applied directly onto the affected area—don’t use both! You must follow all instructions carefully since this medication may cause stomach upset or bleeding if used incorrectly.
6. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a treatment that uses an intense light source to treat melasma. It’s most effective when combined with other treatment forms, like topical creams or chemical peels.
The lasers used for melasma are different from those used for hair removal. They use wavelengths in the blue spectrum and can be pulsed at different frequencies to increase their effectiveness at targeting pigment-producing cells in the skin (melanocytes).
During your laser appointment, you’ll sit comfortably while your doctor applies cooling gel to your face and neck area. You’ll then be guided into position so they can focus on treating the areas with melasma on your face and neck (or wherever else you want them focused).
Afterward, you may feel mild discomfort, but nothing too wrong—just as long as you’re not getting one of those hot lasers! Afterward, there might be some redness or slight swelling, but this will go away within a few hours unless any damage is done, such as burning or blistering after treatment.
7. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are a popular treatment for melasma and other imperfections in the skin. A chemical peel is sometimes done at home, but you should always visit a dermatologist for this procedure.
A chemical peel can remove the top layer of skin and lighten your melasma, although it may cause scarring or sun sensitivity. This treatment is typically effective if you have mild to moderate melasma, but not everyone responds well to chemical peels.
If you decide to try chemical exfoliation as part of your treatment plan, here’s what you need to know:
- Chemical peels can be painful, but they’re also very effective at removing the top layer of skin and lightening melasma.
- You may experience some redness and flaking after your treatment, but this should go away within a few days.
- If you have darker skin tones or have experienced sun damage, chemical peels may not be appropriate for you.
- You should always visit a dermatologist for this procedure.
8. UV Light Treatment
UV light treatment is a non-invasive procedure that uses UV light to improve the appearance of melasma. UV light therapy can be performed at home or in a medical setting, and several different types are available.
If you choose to undergo this type of treatment, your doctor will likely recommend that you complete several treatments, as each session alone may not be enough to give you desired results. In addition, this method may not be covered by insurance and can be expensive.
- In-office treatment: This is done in a doctor’s office or medical spa. It uses a machine that emits light penetrating the skin and treats melasma under your doctor’s supervision. The procedure usually takes about 20 minutes, and you may need two to three weekly sessions for several weeks before seeing results.
- Home-use devices: There are also a number of home-use devices that use LED light or pulsed light technology to treat melasma. While these products are effective, they tend to be more expensive than in-office treatment methods and may not be covered by insurance.
9. Dermabrasion Or Microdermabrasion
Dermabrasion or microdermabrasion. This procedure treats melasma if you have dark spots on your face and are not pregnant. It removes the top layer of skin with a rotating diamond tip or crystals that can remove pigmented cells.
In some cases, this treatment may be combined with lasers, which can help prevent the dark spots from coming back. The recovery time for this procedure depends on how much skin was removed during treatment and what kind of anesthesia was used (if any).
It usually takes one week to heal after dermabrasion, but sometimes there is a scab that needs to be taken off after two weeks, or even more, time has passed since your procedure was done at home by yourself (at-home dermabrasion).
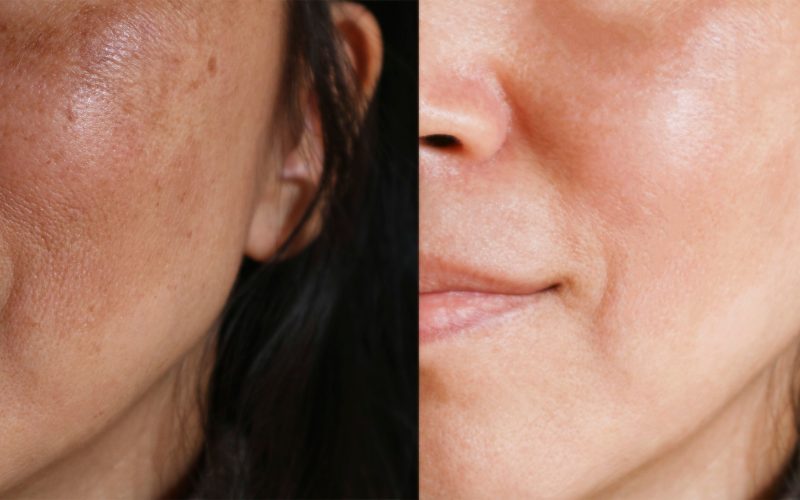
10. Skin-Lightening Procedures
If you have melasma, a dermatologist will likely recommend chemical peels and laser treatments as the most effective treatment. These procedures can be expensive, but they’re also effective at lightening your skin.
For these treatments to work well, you’ll typically need around five sessions about six weeks apart. The costs of these procedures vary depending on where you live, how much time is required for them (some may take longer than others), and whether or not your insurance covers them.
Five Common Mistakes When Treating Melasma
Here are the five biggest mistakes people make when treating their melasma.
1. Using A Product That Contains Too Much Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a chemical used in some skin-lightening products to reduce or eliminate the appearance of dark spots and discoloration. It works by inhibiting melanin production, which is the process that produces skin color.
However, hydroquinone can also cause side effects such as irritation, redness, and blisters if you apply it too often or use too much at once. In addition, some people may not be able to tolerate it because they have an allergy or sensitivity to hydroquinone.
If you’re concerned about using this ingredient in your melasma treatment routine, talk with your doctor before trying any new products so he can help you determine whether hydroquinone suits your skin type and needs.
2. Not Using Sunscreen Or A Sun-Blocking Product Daily
One of the most important steps to prevent melasma is to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen every day, even on cloudy days. If you’re using an over-the-counter product, choose one with an SPF of at least 30 and apply it for 20 minutes before going outdoors. If you’re using a prescription medication, talk to your doctor about how much protection is right for you.
Sunscreen should be applied at least two hours before going outside if you want it to absorb into your skin and provide full coverage; otherwise, it may wear off quickly as soon as it’s exposed to daylight or windblown water droplets from sprinklers or other sources that contain ultraviolet light (which causes sunburn).
3. Starting A New Treatment Without Consulting Your Doctor First
A common mistake is beginning a new treatment without consulting your doctor first. When treating melasma, it’s essential to work with a dermatologist that has experience with the condition and its treatment.
Doctors will help determine whether or not a certain treatment is right for you and can suggest alternatives if it isn’t. They can also help prevent side effects, complications, and other issues by ensuring you’re always on track with your treatment plan.
4. Not Limiting Exposure To UV Radiation
Sun exposure is a common cause of melasma, especially in people with Fitzpatrick skin types I and II. Melasma can worsen with sun exposure, so it’s essential to limit your time outside during the day and wear protective clothing when you do go out.
Be sure to use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on exposed areas of your skin (including your face), and reapply it after being outdoors for an extended period of time.
5. Not Applying The Skin Product Or Treatment In The Right Way
One of the most common mistakes when treating melasma is not correctly applying the skin product or treatment. This can be due to a lack of knowledge or simply because it was not explained properly. How do you apply your skin care product? If you’re using a moisturizer, are you doing so every morning and night?
If you are using a skincare product that contains hydroquinone, do you apply it once or twice daily? This is important because hydroquinone can cause irritation on the skin if it is used improperly.
Conclusion
With so many treatments available, you don’t have to be alone in your fight against this condition. And if none of these remedies work for you, there are other options on the horizon—new drugs and therapies that may help treat melasma in the future. Keep an eye out for these new options and stay up-to-date with any news or breakthroughs in treatment options!